1. (a) A simple classical one-dimensional model for the collision energy dependence of the cross section of a
chemical reaction uses the following expression
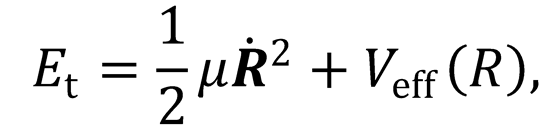
where Et is the initial collision energy, and Veff(R) is the radial dependence of the effective potential. Explain
the origins of this expression, and present arguments to show that the effective potential may be written
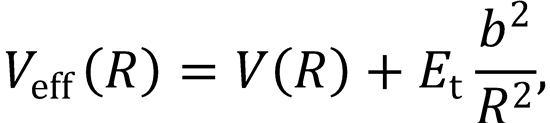
where V(R) is the radial dependence of the potential energy, and b is the impact parameter for the collision.
Recall that the kinetic energy associated with orbital motion can be written 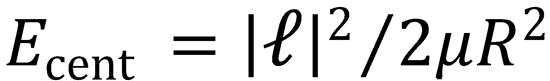
(b) For a reaction between an ion and a molecule, the long range ion-induced dipole interaction potential has
the form
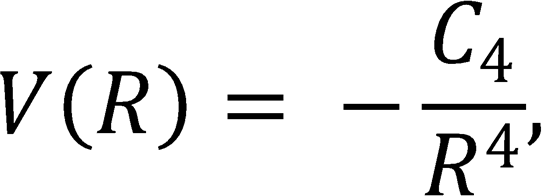
where the coefficient is defined C4 = α'e2/(8πε0), and the constant α' is the polarizability volume of the
molecule. Use this expression, together with equation (12.213) above, to show that the location of the
maximum in the centrifugal barrier on the effective potential is given by the expression
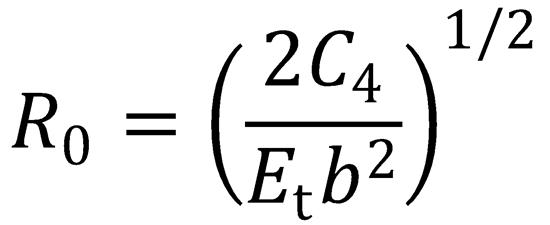
(c) Hence show that, for the radial kinetic energy at the barrier to be greater than zero, the impact parameter
for the ion-molecule reaction is limited by the equation
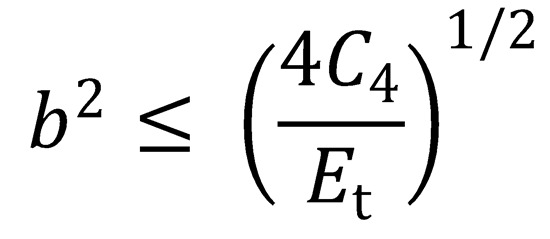
Use this expression to estimate the cross section for the reaction (known as the capture cross section),
stating any additional assumptions made, and sketch the dependence of the cross section on collision
energy (i.e. the excitation function).
(d) The polarizability volume, α', of O2 is 1.4 x 10-30 m3. Estimate the ion-induced dipole contribution to the
capture cross section for the Ca+ + O2 reaction. Employ a mean collision energy corresponding to a
temperature of 10 K.
2. (a) The K-matrix boundary conditions for an s-wave are given in Eq. (12.113),
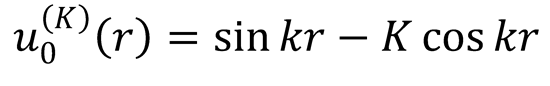
The S-matrix boundary conditions for this wavefunction are
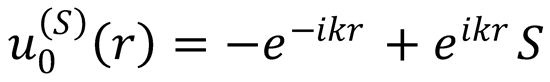
The difference between these boundary conditions is only the normalization of the wavefunction, i.e.,
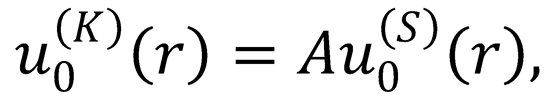
where A is a constant. Derive the relation between the S- and the K-matrix [Eq. (12.117)].
Hint: take the derivative with respect to r of the last equation:
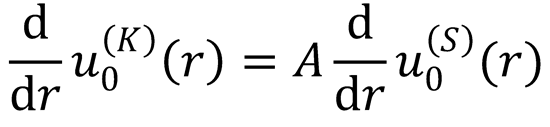
Assume K to be known. For some fixed value of r Eqs. (12.216) and (12.217) are now two equations
linear in A and S, so they can be solved to find S.
Above Problems are available as a PDF to print
Solutions to Chapter 12 Problems